|
___________________________________
Abstract: Network investment and network quality are contradictory. As 1 Introduction of Distributed NodeB Solution
The coverage quality is critical for subscribers, operators are supposed to
Distributed NodeB solution is an economical and fast wireless network CPRI is an open standard interface. In April 2003, Ericsson, Huawei, NEC,
|
|
___________________________________
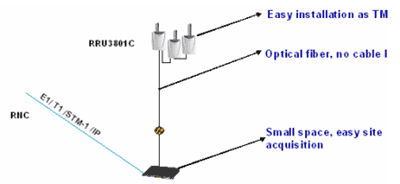
2- Application of 2.1 Partial Outdoor Solution
Operators have their own sites or indoor space, but the equipment rooms are
BBU can be installed at any place within the building, connected with the
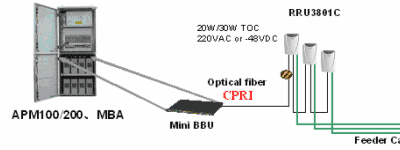
2.2
Operators do not have their own equipment rooms. The adoption of MBA+BBU+RRU
The temperature range for normal working of this solution is: -40~45°C (MBA/APM 2.3 Embedded Outdoor Solution
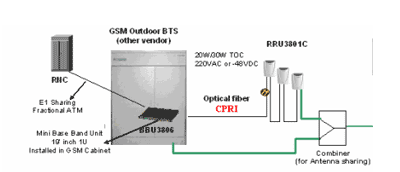
Operators have their own 2G outdoor base station sites and at the same time
The site acquisition, manpower cost, and space leasing cost in the
|
|
___________________________________
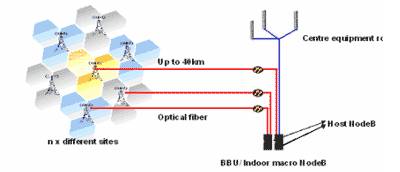
2.4 Inter-Sites Sharing Solution
Operators have optical resource between sites (direction connection or
In this solution, as the handover between sites is softer-handover, which
3- Benefits of
Distributed node B is an important option for the 3G network construction of 1. Solving the problem of equipment rooms
When the operators construct the WCDMA network, the distributed NodeB can 2. Reducing the project implementation cost
The distributed node B features small size, light weight, direct 3. Reducing the operation cost
The distributed node B adopts high efficient amplifier, with the power
The distributed node B has less demand for peripheral facilities such 4. Reducing the equipment cost
The Huawei distributed NodeB solution can solve the problem of burst traffic.
|
|
___________________________________
4-
Since 2002, Huawei started to develop distributed NodeB products( including
Huawei’s distributed NodeB solution can provide economical, fast deployment,
———————–
Huawei is one of the leading players in the global telecom market.
Huawei has about 35,000 employees; its overseas services have covered more
|