|
A Proper Startup for Network Transformation ___________________________________ Xu Huangcheng
NGN planning
I. Traditional carriers are now facing three main challenges: A. Saturation in fixed-line and wireless voice markets. B. C. Lack The need for transformation
The prevalent trend in the telecom market exhibits wireless technologies
The nature of
This of course raises the question of defining clear goals relative to the
‘Convergence’ can be defined as multiple networks of services being combined
|
|
A Proper Startup for Network Transformation ___________________________________ Xu Huangcheng
NGN planning
II.
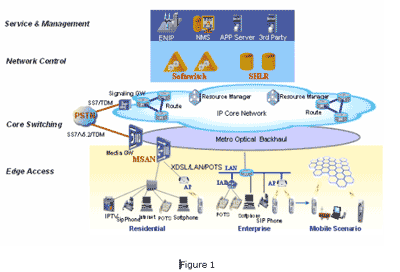
Based on an understanding of future network transformation, Huawei proposes There are four layers to this solution:
1. A 2. The 3. The 4. The
The service and management layer is an open and integrated service platform
The core-switching layer adopts packet switching technology, and provides a
Combining softswitch and SHLR in terms of the solution as a whole brings
|
|
A Proper Startup for Network Transformation ___________________________________ Xu Huangcheng
NGN planning
– Convergence
At the
The service layer enables centralized user profile storage and network call – Broadband oriented Network
MSAN introduces various broadband access methods at the access layer and – Intelligence-oriented Network
At the service layer, the existing separated intelligent networks – fixed,
Initiating network transformation with Softswitch + SHLR + MSAN offers users 1. Simplified network architecture
Serving as independent call control nodes in the traditional local network,
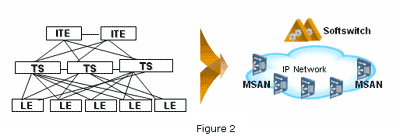
Large capacity softswitch + MSAN denote the most practical and cost
With this solution, one Softswitch system is capable of covering a very
As Figure 2 illustrates, the Softswitch + MSAN solution reduces the number
|
|
A Proper Startup for Network Transformation ___________________________________ Xu Huangcheng
NGN planning
2. Bringing
The SHLR operates in a similar manner to the HLR in a mobile network and the
– Quick and low-cost network-wide coverage of IN services. All calls in the – OPEX is 3. Investment protection
Huawei’s MSAN – key benefits
– MSAN is an integrated access device that can access services such as POTS, – Huawei – The
|
|
A Proper Startup for Network Transformation ___________________________________ Xu Huangcheng
NGN planning
4. Enhancing
With MSAN’s broadband access capability, the network control center Services and capabilities
1. Traditional PSTN/ISDN basic services, supplementary services and Centrex
2. Multimedia Application Services, including point-to-point video services,
3. Value added services include new intelligent phones, iCard integrated
4. Third-party open API. The softswitch and the ENIP platform provide an
The ENIP benefits from flexible and versatile network capability opening 5. Integrated Information and Communication Technology
The convergence of communication and information technologies underpins
IP Centrex: A wide area IP Centrex grouping can be established for a single
UC: UC takes advantage of both real-time communications systems and
Web800: This allows subscribers to call an enterprise’s call center or
Digital home: With the increased move towards broadband network
|
|
A Proper Startup for Network Transformation ___________________________________ Xu Huangcheng
NGN planning
III Further Network Development
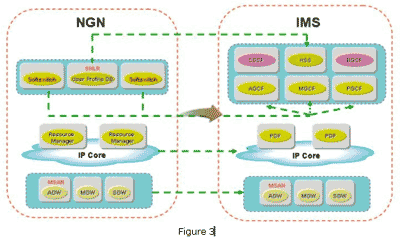
The IMS is the future of
The Softswitch can be upgraded to provide the IMS AGCF/MGCF function
IV Summary
As fixed-line operators are evolving from traditional network carriers to
———————–
Huawei is one of the leading players in the global telecom market.
Huawei has about 35,000 employees; its overseas services have covered more
|